GeForce FX 5900 Ultra

Main differences from the GeForce FX 5800 Ultra
A chip of 135 million transistors : the number of transistors in the chip has not increased much - this indirectly indicated that the changes in the chip based on the NV30 architecture are rather cosmetic.
256-bit local memory interface : Probably the most anticipated new feature in the NV35. Since the release of the NV30, 3D graphics enthusiasts on PC, predicting the performance of the NV35, could not even imagine this chip without a 256-bit local memory exchange interface.
4 advanced pipelined pixel processors: Here, instead of the expected increase in the number of pixel processors to 8, NVIDIA left the same 4 processors. Each of the pixel processors was equipped with: two texture filtering units, two mixed integer and floating point ALUs, and one ALU performing operations only. floating point. That is, only three floating point operations. This configuration made it possible to perform up to 12 pixel operations per clock. However, due to some circumstances, this power only worked in OpenGL, in D3D it was still - only one floating point operation. Of course, it was declared that the new chip was two times superior to NV30 in terms of pixel processor power when executing DirectX9 PS 2.0 pixel shaders with 128-bit computational accuracy.
Intellisample HCT Technology: Local Memory Bandwidth Saving Technique: Lossless compression of the frame buffer, including both color information and from the depth buffer (Z buffer). The possible compression ratio is up to 4:1. Compared to NV30, the Intellisample technology has been improved - as before, the chip determined whether there would be an effect from compressing transmitted data blocks based on several factors, but now, as a result of optimization, the probability of data compression has been increased. Also, under the general name Intellisample HCT, the following techniques were included that increase the efficiency of working with local memory: a local memory controller with a switch, texture caches, early culling of invisible pixels (z-culling), fast clearing the depth buffer (fast z-clear).
UltraShadow Technology : This technology made it possible to speed up the rendering of shadows when using the stencil buffer shadows technique, the same technique used in Doom III. As part of the UltraShadow technology, the ability of the NV30/NV35 chips to double the fillrate was declared, giving out up to 8 pixels per clock, if only the depth buffer and/or stencil buffer is painted over, compared to 4 pixels in normal rendering. The second, most interesting part was the ability to set the depth range in the frame in which the object can cast a shadow. To demonstrate, take a look at the figure:
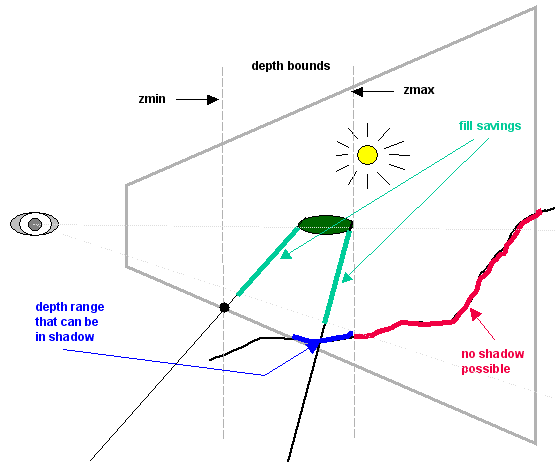
If, when rendering shadows, the pixel depth value stored in the depth buffer did not fall within the specified range, then the stencil buffer for the pixel was not updated. Thus, it became possible to save a fairly large percentage of the filling rate (fillrate). Apparently, to implement this function in the chip, the block responsible for the early rejection of invisible surfaces (early z-cull) was improved, which now checked the value stored in the depth buffer, not only with the current value interpolated based on the coordinates of the triangle, but and with two additional values. As a result, the gain compared to other chips with the same number of pipelines was twofold in the worst case (8 depth buffer values compared to 4 color values) and fourfold (taking into account
Specifications NVIDIA GeForce FX 5900 Ultra
| Name | GeForce FX 5900 Ultra |
| Core | NV35 |
| Process technology (µm) | 0.13 |
| Transistors (million) | 135 |
| Core frequency | 450 |
| Memory frequency (DDR) | 425 (850) |
| Bus and memory type | DDR-256bit |
| Bandwidth (Gb/s) | 27.2 |
| Pixel pipelines | 8(4) |
| TMU per conveyor | 12) |
| textures per clock | 8 |
| textures per pass | 16 |
| Vertex conveyors | 3 |
| Pixel Shaders | 2+ |
| Vertex Shaders | 2+ |
| Fill Rate (Mpix/s) | 3600 |
| Fill Rate (Mtex/s) | 3600 |
| DirectX | 9+ |
| Anti-Aliasing (Max) | SS&MS - 8x |
| Anisotropic Filtering (Max) | 8x |
| Memory | 256MB |
| Interface | AGP 8x |
| RAMDAC | 2x400 MHz |
The NV35 did not complement the existing line from NVIDIA, but replaced the unsuccessful NV30 series. That's what even the president of NVIDIA called the NV30. That is why even the code name does not match what we see, because earlier NV * 5 is a planned improvement of the previous generation, carrying not only bug fixes, but also decent speed gains, as well as architecture improvements.
Knights of the Old Republic




