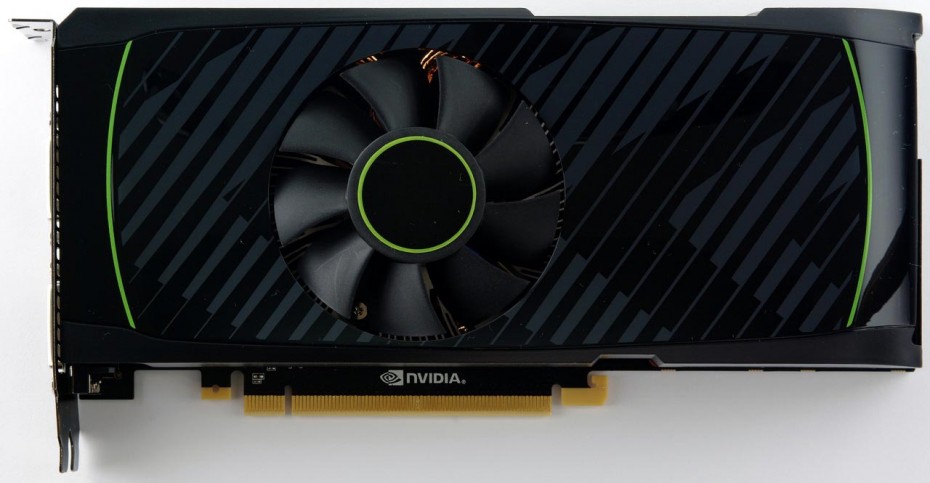
GeForce GTX 560 Ti
As in the case of the GeForce GTX 580/570, the organization of the new core has not changed. Essentially, the GF114 is a fully active GF104 optimized to achieve higher clock speeds while keeping power consumption within reasonable limits.
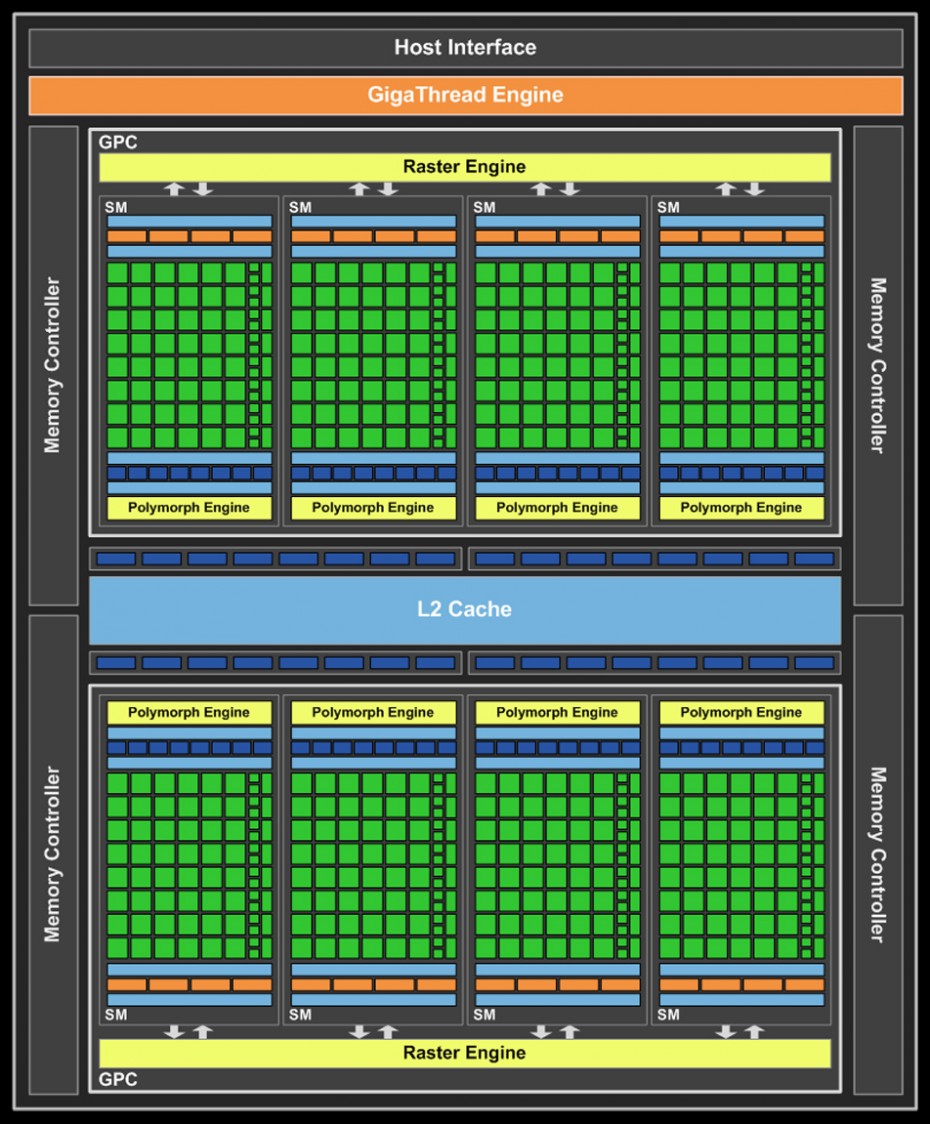
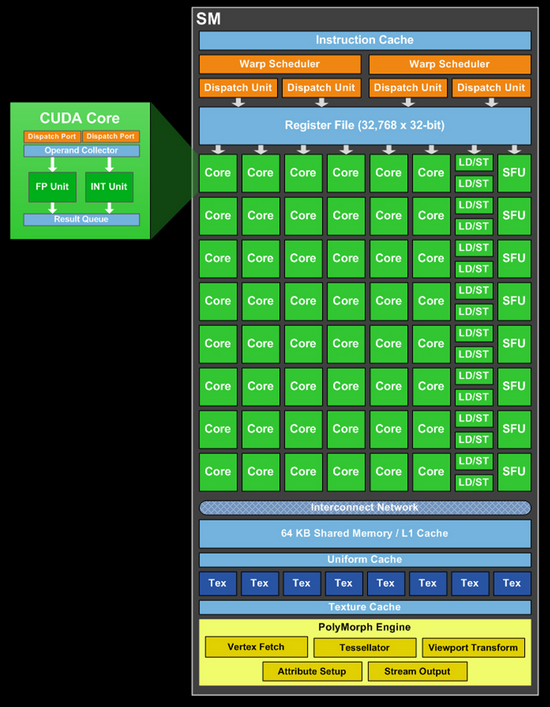
Two GPC clusters include four multiprocessors, each of which, in turn, carries 48 universal thread cores, and, accordingly, the total number of these cores is 384. Each multiprocessor is serviced by eight texture operations units, so the total the number of active TMUs in the new chip is 64. The texture processor architecture has not changed since the GF104. They are capable of full speed FP16 texture filtering, along with the traditional INT8 format. But texture filtering in the FP32 format is four times slower. The volume of the second level cache, as in the GF104, is 512 KB.
In addition, each multiprocessor includes a PolyMorph Engine block, which puts the GF114 head and shoulders above any AMD solution in the field of geometric data processing and tessellation. Even two third-generation tessellation blocks in the Cayman can hardly compete on equal terms with eight GF114 blocks. The configuration of the GF114 raster subsystem remains the same and includes 32 RBE blocks. Since this subsystem is directly connected to the memory subsystem, the latter still consists of four 64-bit controllers, so the total bus width connecting the GPU to the local memory bank is 256 bits.
As for multimedia capabilities, no noticeable innovations were noticed here, but they are, in fact, not needed: the GF104 already knew everything needed by modern standards, including full hardware decoding and scaling of high-definition video in H.264 and VC-1 formats , as well as protected multi-channel audio output in Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio formats via Protected Audio Path. The only significant advantage that AMD can boast in this area is support for DivX hardware decoding.
In general, the GF114 perfectly complies with the principle of "reasonable sufficiency" - it supports all modern graphic and multimedia technologies, but does not contain any rarely requested excesses, such as the ability to simultaneously connect six monitors. In fact, the new mass-produced NVIDIA graphics processor is nothing more than a natural evolutionary development of the ideas embodied in the GF104.
So, it is obvious that the new GeForce GTX 560 Ti in relation to the GeForce GTX 460 1GB is the same as the GeForce GTX 580 and 570 became in relation to the GeForce GTX 480 and GeForce GTX 470, respectively. In other words, this is another "old fairy tale in a new way", however, there is nothing wrong with that, since the Fermi architecture itself is very successful, with the exception, perhaps, of the texture subsystem, which is not very productive compared to the competitor's solutions.
| Specifications NVIDIA GeForce GTX 560 Ti |
|
First of all, the significantly increased clock frequencies of the core are striking - over 800 MHz for the main domain and over 1.6 GHz for the computing one. For NVIDIA solutions, taking into account their architectural features, this is a very serious achievement. Previously, such frequencies were submitted only to individual GeForce models with factory overclocking, but from now on AMD should start to worry seriously, since even the main GF114 domain is faster than the entire core of the Radeon HD 6950. In addition, the latter has only 352 universal VLIW4 processors against 384 scalar ALU for GF114.
The GF114 has 64 texture processors capable of filtering textures in FP16 format at full speed, since each TMU has four filtering units per texture address unit. True, the predecessor of the novelty, the GF104 chip, had the same capabilities in the field of working with textures. Like other NVIDIA solutions, in high-definition video decoding mode, the core frequencies drop to 405/810 MHz, and in idle mode they drop to 51/101 MHz, so in such modes, the GeForce GTX 560 Ti should be expected to be as economical as the GeForce GTX 460 .
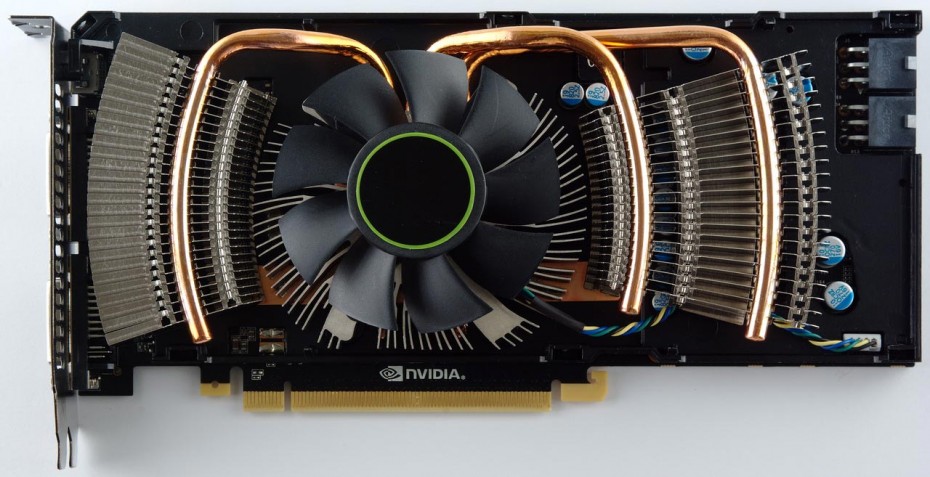
Unfortunately, in the design of the GeForce GTX 560 Ti reference cooling system, the NVIDIA development team decided not to repeat the successful vapor chamber design that worked so well in the GeForce GTX 580 and 570 cooling systems. In this case, a more conservative design with a round central radiator is used. reminiscent of the heatsinks of boxed Intel coolers. With the help of three heat pipes, the central section is connected to two additional arcuate radiators. The blowing of the latter is carried out due to the fact that a conventional axial fan blows not only down, but also to the sides. Note that part of the heated air with this arrangement will be thrown to the right, into the interior of the housing.
The new NVIDIA GeForce GTX 560 Ti did not disappoint: it can be called a worthy addition to the GeForce 500 family. Despite the fact that the recommended price of the GeForce GTX 560 Ti is only $ 249, it is able to fight on equal terms not only with the Radeon HD 6870, against which it was originally was targeted, but also with the more powerful and expensive Radeon HD 6950.