GeForce GTX 580
The new GeForce GTX 580 is nothing revolutionary. The main task that the company's engineers faced was to correct the mistakes made earlier, as well as to increase performance for a more significant lead over the main competitor AMD.

Unfortunately, the first accelerator based on the new architecture, the GeForce GTX 480, did not get all the computing capabilities that NVIDIA engineers put into the GF100 GPU. The fact is that one of the 16 streaming multiprocessors was disabled in the production GTX 480 models, as a result, despite its status, the new top model lost 32 CUDA cores, four texture units and one Polymorph Engine. Most likely, NVIDIA engineers took such a step solely because of production problems that have plagued the company for quite a long time in preparation for the release of solutions based on Fermi. However, now this is not so important, because the new GF110 GPU has at its disposal all 16 SMs, which means 512 full-fledged CUDA cores, 64 TMUs and 16 Polymorph Engine modules. Moreover, NVIDIA engineers have carried out a number of modifications,
The fact is that the texturing speed on the GeForce GTX 480 drops by half when using 64-bit (fp16x4) formats with non-trivial filtering. For example, when texturing from the fp16x4 format with bilinear filtering, the speed drops to 30 pixels per clock (PPC), compared to 60 PPC for 32-bit formats. On the GeForce GTX 580, texturing from such formats occurs at "full speed", i.e. both 32-bit and 64-bit formats with bilinear filtering operate at 64 PPC.
In addition, the GeForce GTX 580 has been improved block rejection of invisible surfaces Z-cull. In the case of the GF100 GPU, when using certain Z-buffer formats, the effectiveness of the Z-cull unit fell. With the introduction of the new Z-cull depth buffer representation formats in the GF110, this issue has been resolved. In general, the increase in the performance of the GeForce GTX 580 relative to the previous flagship GeForce GTX 480 will largely be due to an increase in the number of active functional blocks and an increase in operating frequencies, and to a lesser extent due to architectural improvements related to the strengthening of the Z-Cull block, as well as an increase in the speed of FP16 texture filtering .
Here a completely justified question arises: what about the power consumption of new accelerators, it's no secret that one of the significant drawbacks of the previous flagship - the GeForce GTX 480 was far from the best ratio of performance per watt of energy consumed. In the case of the new GeForce GTX 580, this problem was also solved, as NVIDIA engineers carried out a deep redesign of the GPU, using transistors with lower leakage currents in critical places. This made it possible not only to raise the operating frequencies of the GTX 580 relative to the values of the previous top, but also to reduce the power consumption of the new flagship compared to the GeForce GTX 480.
Like most other modern NVIDIA accelerators, the GeForce GTX 580 fully supports NVIDIA PhysX and CUDA technologies, which allow the use of GPU resources for various kinds of parallel computing, for example, PhysX hardware acceleration is used to enable a number of physical special effects in games based on the PhysX engine. Unfortunately, at the moment there are not so many games that support NVIDIA PhysX technology, although there are some very outstanding projects among them, for example, Batman Arkham Asylum, Mafia II and Metro 2033.
Not to mention NVIDIA Surround and NVIDIA 3DVision Surround technologies. In fact, NVIDIA Surround is a somewhat limited analogue of Eyefinity technology, which AMD announced back in the fall of 2009. The essence of NVIDIA Surround lies in the fact that by connecting three monitors to a computer, the user can combine them into a single workspace, which the system considers as one large monitor. NVIDIA Surround limitations are associated with the inability to combine more than three monitors into a single space, as well as the need to use at least a pair of NVIDIA video cards in SLI mode to activate NVIDIA Surround technology. As for NVIDIA 3DVision Surround,
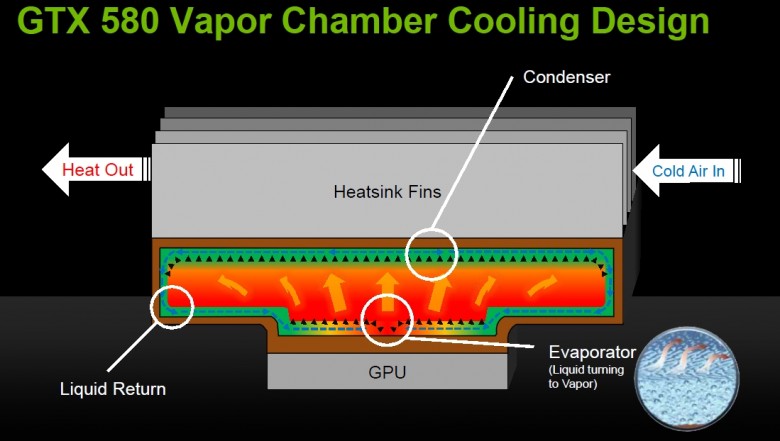
Despite the fact that the new GTX 580 CO is noticeably different from the cooler of the reference version of the GTX 480, the design of the cooling system of the novelty shows the characteristic features inherent in many Hi-End NVIDIA products. As you probably already noticed, the new cooling system of the GTX 580 is devoid of heat pipes that were present in the GeForce GTX 480 CO. This time, the cooling system of the top NVIDIA accelerator is based on the evaporation chamber. The graphics processor is in contact with the platform, directly above which is a sealed compartment - it contains a liquid with a low boiling point. When the temperature rises, the liquid changes its state of aggregation and turns into a gas, transferring heat with it to the top of the cooling system. Cooling slightly, the gas condenses and again turns into a liquid, then the cycle repeats again. In turn, the turbine drives cool air through the heated radiator fins and removes heat outside the case. The video memory, as well as the elements of the power system, are in contact with the metal base of the cooler through special thermal pads.
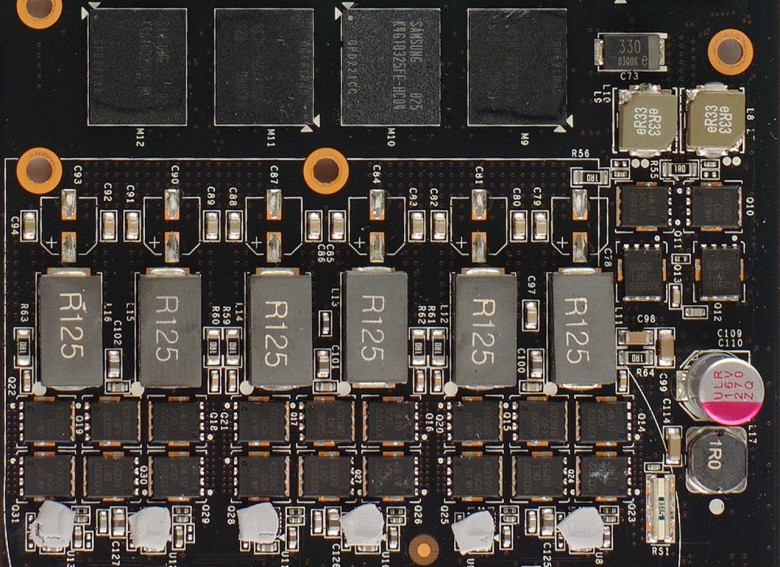
The GF110 graphics processor has six power phases, which are controlled by the CHiL Semiconductor CHL8266 controller, exactly the same was installed on the reference versions of the GeForce GTX 480. The memory is powered according to the 1 + 1 scheme (1 phase Vdd + 1 phase Vddq), controlled by the Anpec APW7066 controller. A similar controller was once used on the GeForce 9800 GTX. In this case, one dual-channel controller controls both video memory voltages (Vdd and Vddq), one channel for each voltage.
The next innovation was the mechanism for hardware monitoring of the current and voltage on the main 12 V video card power lines (6 and 8-pin power connectors, as well as a PCI-Express slot). If excess power is supplied to the video card that exceeds the values allowed by the specifications, the driver automatically reduces the clock frequencies of the accelerator in order to prevent its failure. The manufacturer especially notes the fact that the modern NVIDIA driver automatically reduces the operating frequencies of the accelerator by 50% when running stress testing utilities like OCCT or FurMark. According to NVIDIA engineers, such programs create a critical load on the video card, while real applications never create such a load. That is why it was decided to artificially reduce the frequencies by the drivers. It is also reported that end users will not be given the option to remove this restriction. Unfortunately, at the moment, none of the utilities is able to track the decrease in frequencies caused by the protection mechanism in the drivers, but after the release of the appropriate updates, the user will be able to notice all the changes in the work of the GeForce GTX 580 video cards.

The new GPU frequency is 772 MHz (1544 MHz for the shader domain running at twice the core frequency). This is approximately 10% higher than the operating frequency of the GeForce GTX 480 GF100 (700/1401 MHz). Taking into account the architectural improvements of the GPU, the performance advantage of the GTX 580 may turn out to be more significant.
| Specifications NVIDIA GeForce GTX 580 |
|
It is easy to see that before the release of the GeForce GTX 580, NVIDIA carried out serious and painstaking work to eliminate the obvious shortcomings of the GeForce GTX 480. Reduced power consumption compared to its predecessor, less GPU heating and a fairly quiet cooling system - all this despite the fact that the new product turned out to be significantly faster than the GTX 480, moreover, in many applications, the GTX 580 is more productive than the Radeon HD 5970.