RADEON 8500

The Radeon 8500 was designed to compete with the very best NVIDIA products. ATI. With the release of the RADEON 8500, ATI dealt NVIDIA a very painful blow.
Main characteristics of the ATI RADEON 8500 chip
Manufacturing technology - 0.15 microns;
60 million transistors;
Core operating frequency - 250-300 MHz;
Video memory interface - 128 bit;
Video memory types - SDRAM/SGRAM, DDR SDRAM/SGRAM;
The amount of video memory - 16-256 MB;
Operating frequency of video memory - up to 300 MHz, synchronously with the core;
Support for AGP 2x (3.3V), 4x (1.5B), SBA, DMA, DiME;
Support for ACPI 1.0b, OnNow and IAPC power management.
3D - part
4 pixel pipelines, 2 texture units per pipeline;
Overlay up to 6 textures in one pass, 2 textures per clock;
Support for trilinear and anisotropic filtering;
Support for relief simulation using Emboss, EMBM, Dot3 methods;
Support for full-screen anti-aliasing SMOOTHVISION 2x-6x;
Support for DirectX 8.1 pixel shaders up to 1.4;
Support for DirectX 8.1 vertex shaders up to 1.1;
Hardware block fixed-function T&L ;
Support for TRUFORM technology;
Hidden surface clipping (HSR) support - HYPER Z II.
2D - part
Two built-in CRT controllers;
Built-in RAMDAC with a frequency of 400 MHz;
Built-in TMDS transceiver for connecting digital monitors;
Support for multi-monitor configurations and HYDRAVISION;
Support for MPEG2 hardware decoding (iDCT);
Video-In / Video-Out support when installing ATi Rage Theater chip;
Support for GDI functions, including Windows XP GDI extensions.
In terms of all characteristics, the RADEON 8500 looked, if not more impressive, then at least at the level of NVIDIA GeForce3 Ti500, the king of gaming 3D graphics at that time.
The first thing that immediately catches your eye is that the developers from ATi refused to use three texture modules in the pipeline. Apparently, the sad experience of the RADEON 256, whose third texture module was almost always idle, led ATi to the exact same solution as the one implemented in the GeForce3. The RADEON 8500 can apply up to 6 textures to polygons at once, spending one extra cycle when using more than two textures, and one additional cycle when using more than 4 textures. In exactly the same way, GeForce3 chips (now GeForce3 Ti 200/500) from NVIDIA support up to 4 texture overlays, also having only 2 texture units in pixel pipelines.
The second interesting feature of the RADEON 8500 is full support for multi-monitor configurations. This is the first gaming chip that, along with high performance in 3D, also has full support for multi-monitor configurations.
In general, the RADEON 8500 has both support for new technologies, as well as old ones, proven and "run-in", but improved since the time of the RADEON 256.
The graphics pipeline of the RADEON 8500 as a block diagram :
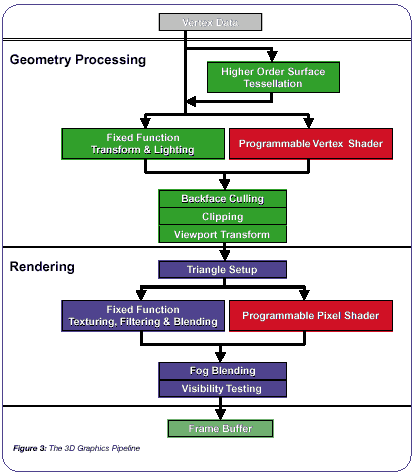
Tessellation (splitting) of triangles is carried out even before processing in the transformation and lighting block, and vertex shaders are already performed on "shredded" triangles. This means that support for TRUFORM technology is not painless and, with a high degree of partitioning, can result in large performance losses, since the number of triangles that has increased many times under the action of TRUFORM can lead to a significant increase in the load on the T&L block and vertex shaders.
TRUFORM
This technology, supported by the hardware of the RADEON 8500, made it possible to improve the quality of models in games by splitting the triangles that make up these models. When splitting, information about the directions of the normals at the vertices of the triangle is used. Based on this information, the RADEON 8500 built an N-Patch, that is, a surface whose curvature is set by control points, and splits it into smaller triangles, the number of which is set by the tessellation level:
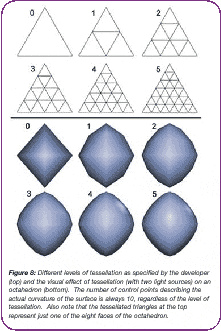
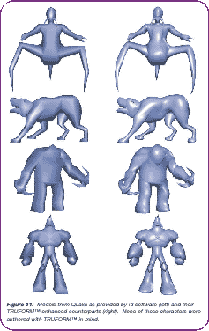
As a result of the TRUFORM action, the model turns out to be smoother and more natural, and, importantly, there is no need to transfer any additional data to the accelerator - in the overwhelming majority of cases, normals are transferred to the accelerator, which uses them, for example, to calculate illumination.
SMARTSHADER
Combines blocks of RADEON 8500 pixel and vertex shaders called PIXEL TAPESTRY II and CHARISMA ENGINE II.
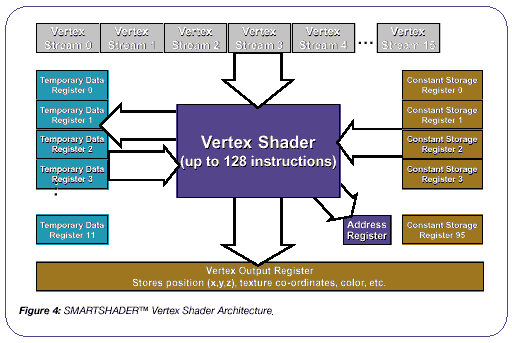
The vertex shader unit of the RADEON 8500, like the GeForce3, was capable of processing shaders up to 128 instructions long and had 96 constant and 12 temporary registers:
The pixel shader unit is more advanced than the GeForce3: it could process shaders up to 22 instructions long, which are translated into pixel shader unit settings - 6 texture sample fetches, 8 address commands and 8 shading commands:
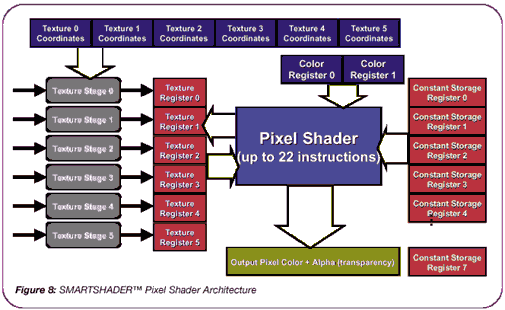
For comparison, the GeForce3 pixel shader unit was able to work with a maximum of 4 textures, and the length of a pixel shader can be a maximum of 12 instructions - 4 fetch operations and 8 shading operations.
In addition, the RADEON 8500 pixel shader unit supported unified addressing and shading commands, which corresponded to DirectX 8.1 1.4 pixel shader specifications.
A simple and understandable conclusion from all this information is that the RADEON 8500 not only supported DirectX 8.0 and DirectX 8.1 pixel and vertex shaders, but, thanks to its enhanced capabilities compared to Geforce3, it could display more "advanced" special effects or deal with complex effects faster than GeForce3.
SMOOTHVISION
A new full-screen anti-aliasing method in the hardware of the RADEON 8500 embodying the ideology of the DirectX 8.0 Multi-Sample Buffer, which, in turn, was a development of the T-Buffer idea from the now deceased 3dfx.
Just like in Voodoo5, the RADEON 8500's full-screen anti-aliasing was based on small displacements of the scene geometry (Vertex Jittering) and the subsequent combination of the colors of the obtained "shifted" samples. However, the implementation of this idea in the RADEON 8500 was more perfect: firstly, the RADEON 8500 could use up to 8 samples to get the color of a pixel (Voodoo5 - up to 4 samples), and secondly, depending on the location of the pixels (a pixel can be located as both on the polygon border and inside it) the RADEON 8500 could choose the optimal number of samples, which made it possible to avoid smoothing the image in those areas where it was not needed.
HyperZ II
HyperZ and HyperZ II were designed to increase the efficiency of the accelerator by cutting off invisible surfaces (Hidden Surface Removal, HSR). That is, if possible, save the core from the need to draw those parts of the scenes that are hidden by closer objects, and therefore there is no point in drawing them.
For example, if any scene in the game consists of two rooms separated by a closed door, and your hero is standing in one of the rooms facing the door, then a poorly optimized game engine will regularly send all the scene polygons to the accelerator for rendering, although the second room closed door is not visible, and the work of rendering the entire interior of that room will be done by the accelerator in vain. The task of HSR is just to rid the accelerator of such useless work as far as possible. And the greater the Overdraw indicator, that is, the degree of overlap of objects in the scene, the greater the gain can be provided by the use of HSR.
| Name | Radeon 8500 |
| Core | R200 |
| Process technology (µm) | 0.15 |
| Transistors (million) | 60 |
| Core frequency | 275 |
| Memory frequency (DDR) | 275 (550) |
| Bus and memory type | DDR-128bit |
| Bandwidth (Gb/s) | 8.8 |
| Pixel pipelines | 4 |
| TMU per conveyor | 2 |
| textures per clock | 8 |
| textures per pass | 3 |
| Vertex conveyors | 2 |
| Pixel Shaders | 14 |
| Vertex Shaders | 1.1 |
| Fill Rate (Mpix/s) | 1100 |
| Fill Rate (Mtex/s) | 2200 |
| DirectX | 8.1 |
| Anti-Aliasing (Max) | SS - 6x (800*600) |
| Anisotropic Filtering (Max) | 16x |
| Memory | 64 / 128 MB |
| Interface | AGP4x |
| RAMDAC | 400 / 240 MHz |
NVIDIA finally has a worthy competitor. ATI RADEON 8500 boards were not inferior in performance to boards based on NVIDIA GeForce3 Ti500. At the same time, the RADEON 8500, like the GeForce3, not only complied with the Direct X 8.1 specifications, but also had new 3D technologies designed to improve the image quality. These were, for example, TRUFORM and SMOOTHVISION, which are not supported by the GeForce3 Ti500/200.
Return To Castle Wolfenstein




