Radeon HD 5870
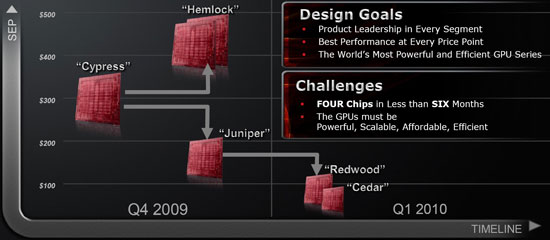
AMD marked the beginning of the development of a generation of graphics chips of the Evergreen family (evergreen). For a better perception by users, AMD marketers decided to abandon the alphanumeric designations of their GPUs and now all the company's graphic novelties have their own names. The first representative of the new family is a chip codenamed Cypress (Cypress), which should become the basis of flagship graphics accelerators with a single GPU.
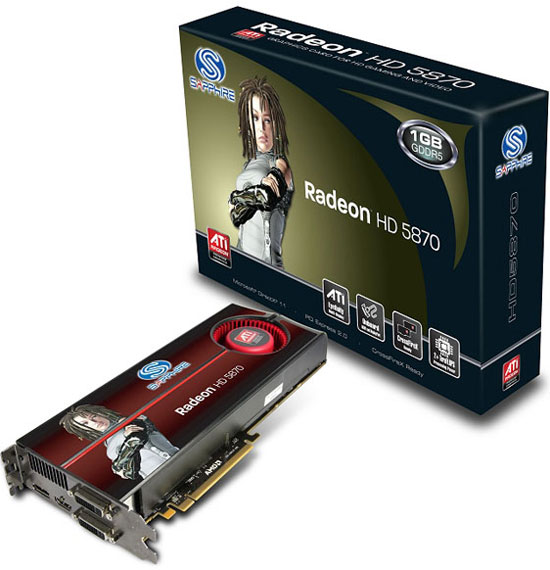

Hemlock chips (hemlock - American conifer), Juniper (juniper), Redwood (mahogany) and Cedar (cedar) will appear later, which should occupy all other market niches, from low-cost to Ultra Hi-End solutions. Thus, for about half a year, AMD plans to conduct an active campaign to win over our preferences.
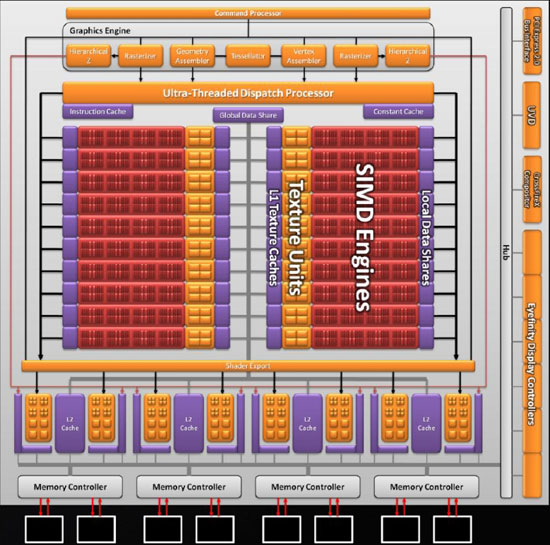
The Cypress chip, which is the basis for the AMD Radeon HD 5870, is not just a slightly modified RV770 under the new label. This is a completely new solution, significantly redesigned at the hardware level compared to the RV770/RV790. To successfully promote a novelty on the world market, it must have not only high performance, but also a number of other, sometimes no less important consumer characteristics, such as functionality, high-quality visualization modes and support for modern technologies. Let's take a look at how AMD engineers have moved forward with the development of the Cypress chip and the Radeon HD 5870 graphics accelerator built on its basis.
Cypress GPU Block Diagram
Support for Microsoft DirectX 11
The AMD Radeon HD 5870 is the world's first GPU to support all the features of the DirectX 11 API set. Below is an excerpt from AMD's slides demonstrating the key differences between DirectX 11 and DirectX 10 and 10.1

It is worth noting that all AMD solutions that support DX 11 are fully compatible with previous versions of DirectX. So, let's see what is radically new in the eleventh version.
Hardware tessellation
Applied to 3D graphics, tessellation is the process of breaking an image into smaller shapes, such as triangles or quadrilaterals. The use of tessellation in computer games is due to the need to increase the level of detail of three-dimensional objects. Before the advent of DirectX 11 and compatible hardware, the use of tessellation significantly loaded the memory subsystem and drives, since it required the transfer of huge amounts of data. A modern approach to tessellation should significantly reduce memory bandwidth requirements and make it possible to actively use tessellation in the latest computer games.
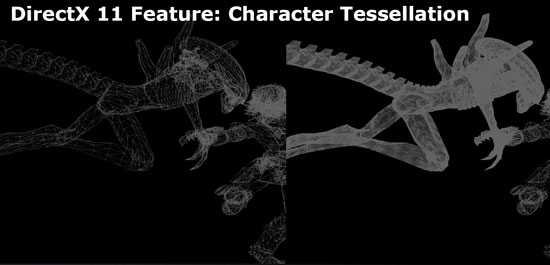
I must say that the tessellation block is present in AMD graphics accelerators starting with the Radeon HD 2900XT, but, unfortunately, its use in the DirectX 11 environment is impossible. For tessellation in DirectX 11, additional calculation stages are used - Hull Shader (surface shader) and Domain Shader (regional or zone shader), which cannot be performed on accelerators of previous generations, so the existing hardware tessellation unit was not useful.
In addition to the obvious visual bonuses, one more pleasant fact should be noted - scalability. Let's imagine a model, the data about which is passed to the GPU for processing, in particular, to the tessellation block. This block, depending on the performance level of a particular GPU, can vary the number of object splits in order to keep the overall performance at an acceptable level.
Multi-threaded rendering
It is no secret to anyone that one of the most effective methods to increase the performance of computing technology is the simultaneous processing of multiple data streams. The most striking example is multi-core processors, which have recently become truly accessible to the masses of consumers. Now it's time to think about how to use the resources of modern GPUs more efficiently to speed up the rendering of 3D graphics in games. While DirectX 10 only allows rendering commands to be passed from a single thread, DirectX 11 implements multi-threaded rendering, which makes it possible to create so-called display lists from multiple threads and execute them from the main rendering thread.
Texture compression
The texture compression methods implemented in DirectX 10 and earlier do not render 3D worlds at the required level of quality. That is why developers have introduced new texture compression formats in DirectX 11 - BC6 (for working with HDR textures) and BC7 (narrow dynamic range of RGB or RGBA textures). New methods allow game developers to use significantly larger textures, and the use of textures with a wide dynamic range will significantly improve the quality of the picture.
Eyefinity Technology
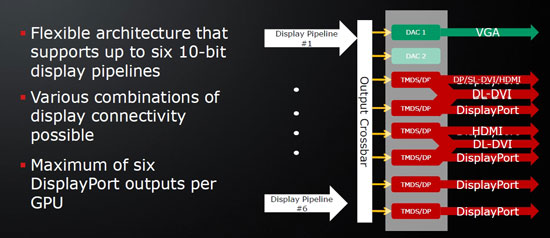
Developers have been working on improving the perception of computer games for decades. Virtual reality helmets, virtual glasses and even character control systems using the power of thought - we have already gone through all this. Unfortunately, so far none of these solutions can boast of mass demand. Each approach has a number of advantages, which, unfortunately, do not cover the disadvantages. With the release of the Radeon HD 5870, AMD offers its own version of expanding the boundaries of visual perception of computer games through Eyefinity technology (however, this technology can be successfully used not only in games). Let's see what exactly AMD offers us.

A special hardware complex allows you to connect up to six monitors to one new-generation video card, while it is possible to create various connection configurations. The number and type of connectors on a particular board may vary, depending on the preferences of the manufacturer.

Eyefinity technology can work with both windowed and full-screen 3D applications. Moreover, according to AMD, to support this technology in computer games, you do not need to install any specialized patches or additional drivers. All you need is support for high resolutions in the game itself.
With the right placement and proper choice of monitors, in games with high-resolution support, the user should be almost completely immersed in the game thanks to the work of the so-called peripheral vision.
FSAA and anisotropic filtering
One of the methods for improving image quality in modern games is full-screen anti-aliasing (Antialiasing, or AA). Since the use of various AA methods requires additional efforts from the 3D accelerator, it is vital to maintain a comfortable level of performance when one or another anti-aliasing method is enabled. AMD's new HD 58xx series solutions provide nearly double the performance in various MSAA (Multi Sample Antialiasing) modes compared to the previous generation HD 48xx. In addition, now the user can use the so-called supersampling, which was used at the dawn of the development of 3D accelerators, but has given way to more economical anti-aliasing methods, although it surpassed them in quality. The essence of this method is that the frame is rendered in resolution, exceeding the resolution set in the game. Now that memory bandwidth has increased significantly, this method is experiencing a rebirth. In the future, we will have to figure out all the subtleties of the modern implementation of SSAA.

Another important factor is anisotropic texture filtering. According to AMD engineers, the new filtering algorithm ensures perfect quality without performance loss. There are currently several anisotropic filtering modes available in drivers.
The GPU runs at 825 MHz and contains 1600 stream processors, that is, twice as many as the RV770. The new GPU contains 2.1 billion transistors, which is also almost double that of the RV770 (956 million). The Radeon HD 5870 will feature GDDR5 memory that runs at 1300 MHz (or 5200 MHz in DDR mode) for 150 GB/s of bandwidth. The card consumes about 180W in 3D modes and only 27W in idle mode, clearly less than the Radeon HD 4870 (90W).
Specifications ATI Radeon HD 5870
| Name | Radeon HD 5870 |
| Core | Cypress |
| Process technology (µm) | 40 |
| Transistors (million) | 2100 |
| Core frequency | 825 |
| Memory frequency (DDR) | 1300 (5200QDR) |
| Bus and memory type | GDDR5 256-bit |
| Bandwidth (Gb/s) | 150 |
| Unified shader blocks | 1600 |
| Frequency of unified shader units | 750 |
| TMU per conveyor | 80 |
| ROP | 32 |
| Shader Model | 5.0 |
| Fill Rate (Mtex/s) | 30000 |
| DirectX | 11.0 |
| Memory | 1024/2048 |
| Interface | PCIe 2.0 |
The new video adapter ATI Radeon HD 5870 turned out to be a success: according to the results of most tests, it confidently outperformed the current top single-chip solutions (we are talking about the HD 4890 and GTX 285), and sometimes could compete with dual-chip solutions. The advantages of the HD 5870 include a very low noise level, as well as moderate power consumption, which makes it an excellent choice for a gaming PC.



